Antioxidants: Why You Should Take Them Regularly
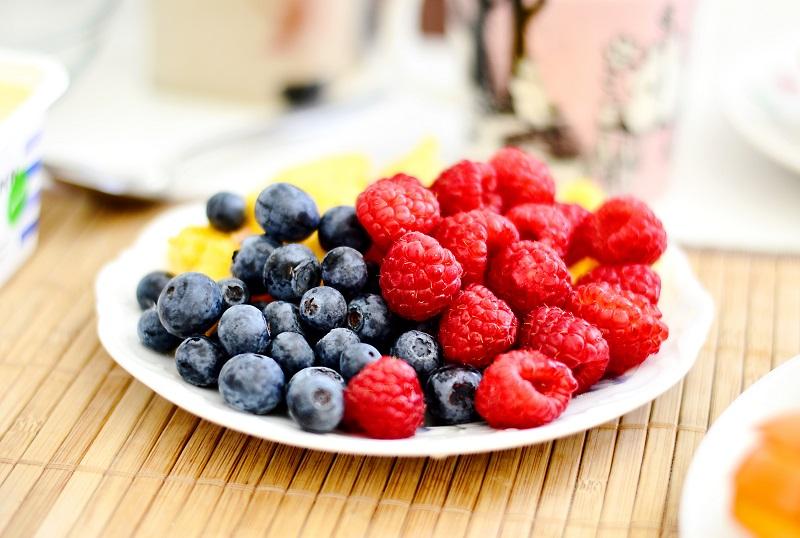
Recent research shows that red berries and vegetables have the potential to provide health benefits for numerous conditions. Most notably, they can help to prevent the development and progression of cardiovascular disease and cancer as well as age-related diseases.
Red berries and vegetables are rich in antioxidants and phenolic compounds. These components provide the anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic and anti-mutagenic properties that are responsible for the many health benefits of these foods. They’re also a rich source of dietary fibre and other essential nutrients such flavonoids, catechins, procyanidins, carotenoids and Vitamin C. These are the compounds which protect the plant against diseases and also provide the vibrant red, purple or blue colours, flavours and aromas of the antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables.
Benefits of antioxidants
Berries are potentially useful for inhibiting the growth of intestinal pathogens due to their natural, potent antimicrobial agents. Carcinogenesis and oxidative lesions also occur in the body and accumulate with age, thus increasing the risk of cancer. The antioxidant content of certain fruits and vegetables may reduce the oxidative damage that occurs with age and therefore reduce the risk of cancer.
Potent antioxidants have also long been known to improve memory and reduce the development and progression of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease. They also protect the eyes and prevent age-related vision problems. Other benefits of increasing your intake of antioxidants include:
- Slower signs of ageing, especially of the skin, eyes, tissue, joints, heart and brain
- Healthier, more youthful, and glowing skin
- Reduced cancer risk
- Detoxification support
- Longer life span
- Protection against heart disease and stroke
- Less risk for cognitive problems such as dementia
- Reduced risk for vision loss or disorders like macular degeneration and cataracts
How antioxidants protect our health
Antioxidant sources such as antioxidant foods, herbs, spices and teas, reduce the effects of free radicals (also called oxidative damage/stress) which play a major role in disease formation. The leading health problems facing us today (conditions like heart disease, cancer and dementia) have been linked to increased levels of oxidative damage and inflammation. In simple terms, oxidation is a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals, leading to other chemical chain reactions that damage cells.
Sources of antioxidants in your diet offer much-needed help in counteracting the damage done by factors like excess sun exposure, a poor diet, smoking, alcohol or drug use, certain medications, toxicity or chemical exposure, and even high amounts of stress and other natural factors that increase the risk of age-related problems. In the process of fighting free radical damage, antioxidants protect healthy cells while halting the growth of malignant or cancerous cells.
Best natural antioxidant sources
Most foods will contain a small amount of naturally occurring antioxidants. However, here is a list of the most potent ones:
- Fruits - blackberries, strawberries, blueberries, boysenberries, loganberries, mulberries, pomegranates, raspberries, plums, oranges, cherries, grapes, goji berries and cranberries
- Vegetables - capsicums, artichokes, carrots, kale, spinach, Brussel sprouts, alfalfa sprouts, broccoli, beetroot and onions
- Spices and herbs - turmeric, ginger, garlic, coriander, basil, parsley, green tea, cayenne, cloves, cinnamon, cumin and oregano
- Other foods - cacao, red wine and kidney beans